Bonfire 2018, The Hague, Preparations On 31 December 2017 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor
A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor
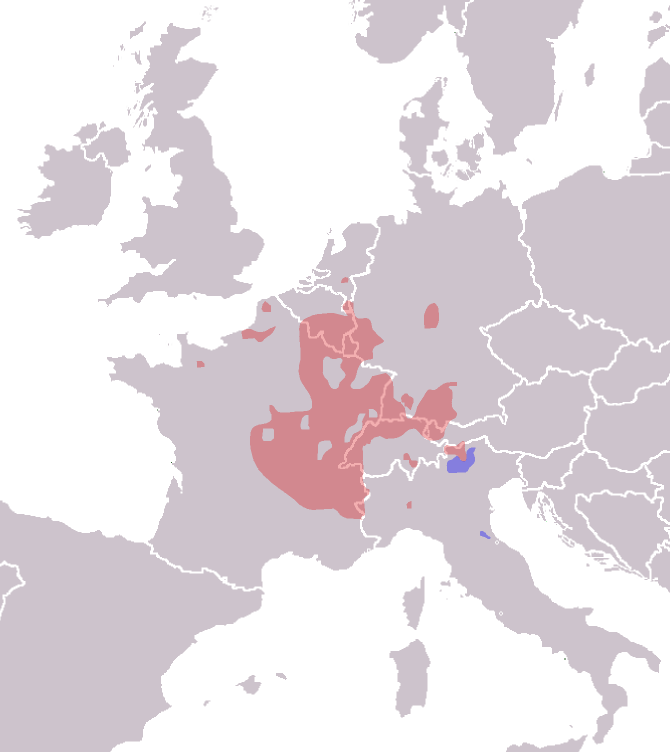 Bonfire traditions of early spring, lit on the Sunday following Ash Wednesday (, otherwise called
Bonfire traditions of early spring, lit on the Sunday following Ash Wednesday (, otherwise called
''
''.
 In
In
 Bonfire in Nepal is taken almost synonymous with camp-fire. During winter months its quite common to have a bonfire in hotels, resorts, and residential areas, as well as private properties.
Bonfires are also lit during Siva ratri in the evening. This holiday is based on the lunar calendar and often falls during month of February.
Bonfire in Nepal is taken almost synonymous with camp-fire. During winter months its quite common to have a bonfire in hotels, resorts, and residential areas, as well as private properties.
Bonfires are also lit during Siva ratri in the evening. This holiday is based on the lunar calendar and often falls during month of February.
 In
In
 In the
In the  The annual rock and dance music
The annual rock and dance music
 In
In
Dancing May Day Through History
{{Authority control Halloween events Seasonal traditions Summer traditions Types of fire

 A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor
A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames a ...
, used either for informal disposal of burnable waste material or as part of a celebration.
Etymology
The earliest recorded uses of the word date back to the late 15th century, with theCatholicon Anglicum
The ''Catholicon Anglicum'' is an English-to-Latin bilingual dictionary compiled in the late 15th century.
History
Writing and publishing
The ''Catholicon Anglicum'' was written in 1483. Its author was anonymous at the time of its writing ...
spelling it as ''banefyre'' and John Mirk
John Mirk was an Augustinian Canon Regular, active in the late 14th and early 15th centuries in Shropshire. He is noted as the author of widely copied, and later printed, books intended to aid parish priests and other clergy in their work. The ...
's ''Book of Festivals'' speaking of a communal fire in celebrations of Saint John's Eve
Saint John's Eve, starting at sunset on 23 June, is the eve of celebration before the Feast Day of Saint John the Baptist. The Gospel of Luke (Luke 1:26–37, 56–57) states that John was born six months before Jesus; therefore, the feast of J ...
that "was clene bones & no wode & that is callid a bone fyre". The word is thus a compound of "bone" and "fire."
In 1755, Samuel Johnson misattributed the origin of the word as a compound of the French "''bon''" (“good”) and the English "fire" in A Dictionary of the English Language.
Regional traditions
In many regions of continental Europe, bonfires are made traditionally on 24 June, thesolemnity
In the liturgical calendar of the Roman Rite, a solemnity is a feast day of the highest rank celebrating a mystery of faith such as the Trinity, an event in the life of Jesus, his mother Mary, his earthly father Joseph, or another important sai ...
of John the Baptist
John the Baptist or , , or , ;Wetterau, Bruce. ''World history''. New York: Henry Holt and Company. 1994. syc, ܝܘܿܚܲܢܵܢ ܡܲܥܡܕ݂ܵܢܵܐ, Yoḥanān Maʿmḏānā; he, יוחנן המטביל, Yohanān HaMatbil; la, Ioannes Bapti ...
, as well as on Saturday night before Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel ...
. Bonfires are also a feature of Walpurgis Night
Walpurgis Night (), an abbreviation of Saint Walpurgis Night (from the German ), also known as Saint Walpurga's Eve (alternatively spelled Saint Walburga's Eve), is the eve of the Christian feast day of Saint Walpurga, an 8th-century abbess ...
in central and northern Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, and the celebrations on the eve of St. John's Day in Spain. In Sweden bonfires are lit on Walpurgis Night
Walpurgis Night (), an abbreviation of Saint Walpurgis Night (from the German ), also known as Saint Walpurga's Eve (alternatively spelled Saint Walburga's Eve), is the eve of the Christian feast day of Saint Walpurga, an 8th-century abbess ...
celebrations on the last day of April. In Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
bonfires are tradition on Midsummer Eve and to a lesser degree in Easter.
Alpine and Central Europe
 Bonfire traditions of early spring, lit on the Sunday following Ash Wednesday (, otherwise called
Bonfire traditions of early spring, lit on the Sunday following Ash Wednesday (, otherwise called Quadragesima Sunday Quadragesima Sunday (also known as Invocabit Sunday) is the first Sunday in Lent, occurring after Ash Wednesday.
The term ''Quadragesima'' is derived from the Latin word for "fortieth", as there are exactly forty days from Quadragesima Sunday until ...
), are widespread throughout the Alemannic German speaking regions of Europe and in parts of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
. The burning of "winter in effigy" at the Sechseläuten
The ''Sechseläuten'' (Zürich German: ''Sächsilüüte'', "The six o'clock ringing of the bells") is a traditional spring holiday in the Swiss city of Zürich celebrated in its current form, usually on the 3rd Monday of April, since the early 2 ...
in Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
(introduced in 1902) is inspired by this Alemannic tradition. In Austria, the custom of the "'' Osterfeuer''" or Easter fires is widespread, but also regulated in some cities, districts and countries to hold down the resulting annual peak of PM10-dust emission. There are also "" (solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
fires) ignited on the evening of 21 June.
Since 1988 "" (fires in the Alps) have been lit on a day in August on mountains so they can be seen from afar as an appeal for sustainable development of mountain regions.
In the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
, the festival called "Burning the Witches" (also Philip and Jacob Night, Walpurgis Night
Walpurgis Night (), an abbreviation of Saint Walpurgis Night (from the German ), also known as Saint Walpurga's Eve (alternatively spelled Saint Walburga's Eve), is the eve of the Christian feast day of Saint Walpurga, an 8th-century abbess ...
, or Beltane
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking the ...
) takes place on the night between 30 April and 1 May. This is a very old and still observed folk custom and special holiday. On that night, people gather together, light bonfires, and celebrate the coming of spring. In many places people erect maypoles.
The night between 30 April and 1 May was considered magical. The festival was probably originally celebrated when the moon was full closest to the day exactly between the spring equinox and summer solstice. People believed that on this night witches fly to their Sabbath, and indeed this is one of the biggest pagan holidays. People also believed, for example, in the opening of various caves treasures were hidden. The main purpose of this old folk custom was probably a celebration of fertility.
To protect themselves against witches, people lit bonfires in high places, calling these fires "Burning the Witches". Some people took to jumping over the fire in order to ensure youth and fertility. The ash from these fires supposedly had a special power to raise crops, and people also walked their cattle through the ashes to ensure fertility.
Australia
In Australia, bonfires are rarely allowed in the warmer months due to fire danger. Legislation about bonfires varies between states, metropolitan and rural regions, local government areas, and property types. For example, in urban areas of Canberra bonfires may be lit around theQueen's Official Birthday
The King's Official Birthday (alternatively the Queen's Official Birthday when the monarch is female) is the selected day in the United Kingdom and most Commonwealth realms on which the birthday of the monarch is officially celebrated in those ...
if local fire authorities are notified; however, they are banned the rest of the year. Smaller fires such as campfire
A campfire is a fire at a campsite that provides light and warmth, and heat for cooking. It can also serve as a beacon, and an insect and predator deterrent. Established campgrounds often provide a stone or steel fire ring for safety. Campfires ...
s and outdoor barbecues are usually permitted outside of fire restriction periods. In the state of Queensland, the rural town of Killarney hosts an annual Bonfire night for the greater community; proceeds support the town's aged care facilities.
Canada
Due to their historic connection to Britain and Ireland, the province ofNewfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic region. The province comprises t ...
has many communities that celebrate bonfire nights, particularly Guy Fawkes Night; this is one of the times when small rural communities come together. In the province of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, many communities light bonfires on 24 June to celebrate Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day
Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day (french: Fête de la Saint-Jean-Baptiste, la Saint-Jean, Fête nationale du Québec), also known in English as ''St John the Baptist Day'', is a holiday celebrated on June 24 in the Canadian province of Quebec and by Fren ...
.
France
InFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, the bonfire celebrates Jean le Baptiste during the ("St John's Day"), first Saturday after the solstice, about 24 June. Like the other countries, it was a pagan celebration of the solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
, or midsummer
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer usually held at a date around the summer solstice. It has pagan pre-Christian roots in Europe.
The undivided Christian Church designated June 24 as the feast day of the early Christian martyr ...
, but Christianisation transformed it into a Catholic celebration.
India
InIndia
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, particularly in Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
, people gather around a bonfire and eat peanuts and sweets during the festival of Lohri
''Lohri'' is a popular winter Punjabi folk festival celebrated primarily in Northern India. The significance and legends about the Lohri festival are many and these link the festival to the Punjab region. It is believed by many that the festiva ...
to celebrate the winter solstice which occurred during the Indian month of Magh. People have bonfires on communal land. If there has been a recent wedding or a new born in the family, people will have a bonfire outside their house to celebrate this event. The festival falls in the second week of January every year. In the northeastern state of Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
, the harvest festival of Bhogali Bihu
Magh Bihu (মাঘ বিহু) (also called Bhogali Bihu (ভোগালী বিহু) (of eating Bhog i.e. enjoyment) or Maghar Domahi (মাঘৰ দোমাহী) is a harvest festival celebrated in Assam, North-East India, w ...
is celebrated to mark the end of the harvest season
The harvesting of wine grapes (Vintage) is one of the most crucial steps in the process of wine-making. The time of harvest is determined primarily by the ripeness of the grape as measured by sugar, acid and tannin levels with winemakers basing t ...
in mid-January. In southern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, particularly in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
and Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
, the Bhogi Festival is celebrated on the last day of Maarkali, which is also the first day of the farming festival of Pongal Pongal may refer to:
* Pongal (festival), an annual Tamil festival
* Pongal (dish)
Pongal, also known as pongali or huggi, is an Indian rice dish. In Tamil, "pongal" means "boil" or "bubbling up". The two varieties of pongal are ''chakarai pong ...
. People collect unwanted items from their houses and throw them into a bonfire to celebrate. During the ten days of Vijayadashami
Vijayadashami ( sa, विजयदशमी, Vijayadaśamī, translit-std=IAST), also known as Dussehra, Dasara or Dashain, is a major Hindu festival celebrated at the end of Navaratri every year. It is observed on the tenth day in the Hind ...
, effigies of Ravana
Ravana (; , , ) is a rakshasa king of the island of Lanka, and the chief antagonist of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana'' and its adaptations.
In the ''Ramayana'', Ravana is described to be the eldest son of sage Vishrava and rakshasi Kaikesi. ...
, his brother Kumbhakarna
Kumbhakarna (Sanskrit: कुम्भकर्ण, lit. ''pot-eared'') is a powerful rakshasa and younger brother of Ravana from the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Despite his gigantic size and appetite, he is described as a virtuous character an ...
and son Meghanad are erected and burnt by enthusiastic youths at sunset. Traditionally a bonfire on the day of Holi
Holi (), also known as the Festival of Colours, the Festival of Spring, and the Festival of Love,The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...". is an ancient Hindu religious festival ...
marks the symbolic annihilation of Holika
Holika ( sa, होलिका, translit=Hōlikā), also known as Simhika, is an asuri in Hinduism. She is the sister of the asura-kings Hiranyakashipu and Hiranyaksha, and the aunt of Prahlada.
The legend of '' Holika Dahan'' (Holika's bur ...
the demoness
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in Media (communication), media such as comics, video ...
as described above.Origins of Holi''
BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Iran
Chaharshanbe Suri
Chaharshanbeh Suri or Charshanba Suri ( fa, چهارشنبهسوری, Čahāršanbe suri; ), is an Iranian festival of the fire dance celebrated on the eve of the last Wednesday of the year. It is the first festivity of the Nowruz Celebrat ...
is a fire jumping festival celebrated by Persian people, Kurdish people and some other ethnicities. The event takes place on the eve of the last Wednesday before Nowruz
Nowruz ( fa, نوروز, ; ), zh, 诺鲁孜节, ug, نەۋروز, ka, ნოვრუზ, ku, Newroz, he, נורוז, kk, Наурыз, ky, Нооруз, mn, Наурыз, ur, نوروز, tg, Наврӯз, tr, Nevruz, tk, Nowruz, ...
. Loosely translated as Wednesday Light, from the word , which means light in Persian, or more plausibly, consider to be a variant of (red) and take it to refer either to the fire itself or to the ruddiness (sorkhi), meaning good health or ripeness, supposedly obtained by jumping over it, is an ancient Iranian festival dating back to at least 1700 BCE of the early Zoroastrian era. Also called the Festival of Fire, it is a prelude to Nowruz, which marks the arrival of spring. The words Chahar Shanbeh mean Wednesday and Suri means red. Bonfires are lit to "keep the sun alive" until early morning. The celebration usually starts in the evening, with people making bonfires in the streets and jumping over them singing "". The literal translation is, my yellow is yours, your red is mine. This is a purification rite. Loosely translated, this means you want the fire to take your pallor, sickness, and problems and in turn give you redness, warmth, and energy. There are Zoroastrian religious significance attached to Chahārshanbeh Suri and it serves as a cultural festival for Iranian and Iranic people.
Another tradition of this day is to make special Chaharshanbe Suri Ajil, or mixed nuts and berries. People wear disguises and go door to door knocking on doors as similar to Trick-or-treating. Receiving of the Ajeel is customary, as is receiving of a bucket of water.
Ancient Persians celebrated the last 5 days of the year in their annual obligation feast of all souls, Hamaspathmaedaya (Farvardigan or popularly Forodigan). They believed Faravahar, the guardian angels for humans and also the spirits of dead would come back for reunion. There are the seven Amesha Spenta, that are represented as the haft-sin (literally, seven S's). These spirits were entertained as honored guests in their old homes, and were bidden a formal ritual farewell at the dawn of the New Year. The festival also coincided with festivals celebrating the creation of fire and humans. In Sassanid period the festival was divided into two distinct pentads, known as the lesser and the greater Pentad, or Panji as it is called today. Gradually the belief developed that the 'Lesser Panji' belonged to the souls of children and those who died without sin, whereas 'Greater Panji' was truly for all souls.
Iraq
In Iraq, Assyrian Christians light bonfires to celebrate theFeast of the Cross
In the Christian liturgical calendar, there are several different Feasts of the Cross, all of which commemorate the cross used in the crucifixion of Jesus. Unlike Good Friday, which is dedicated to the passion of Christ and the crucifixion, th ...
. In addition to the bonfire, every household traditionally hangs a lighted fire in the roof of their house.
Ireland
ThroughoutIreland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, bonfires are lit on the night of 31 October to celebrate Halloween or Samhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year ...
. Bonfires are also held on 30 April, particularly in Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
to celebrate the festival of Bealtaine
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking th ...
and on St. John's eve, 23 June, to celebrate Midsummer's eve
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer usually held at a date around the summer solstice. It has pagan pre-Christian roots in Europe.
The undivided Christian Church designated June 24 as the feast day of the early Christian mar ...
, particularly in County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns a ...
where it is also known as 'Bonna Night'.
In Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
, bonfires are lit on Halloween, 31 October, and each 11 July, bonfires are lit by many Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
communities to celebrate the victory of Williamite
A Williamite was a follower of King William III of England (r. 1689–1702) who deposed King James II and VII in the Glorious Revolution. William, the Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, replaced James with the support of English Whigs.
O ...
forces at the Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ga, Cath na Bóinne ) was a battle in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II of England and Ireland, VII of Scotland, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and J ...
, which took place on 12 July 1690. This is often called the "Eleventh night
In Northern Ireland, the Eleventh Night or 11th Night, also known as "bonfire night", is the night before the Twelfth of July, an Ulster Protestant celebration. On this night, large towering bonfires are lit in Protestant loyalist neighbourhood ...
". Bonfires have also been lit by Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
communities on 9 August since 1972 to protest and commemorate Internment.
Israel
 In
In Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, on the eve of Lag BaOmer
Lag BaOmer ( he, , ''LaG Bāʿōmer''), also Lag B'Omer or Lag LaOmer, is a Jewish religious holiday celebrated on the 33rd day of the Counting of the Omer, which occurs on the 18th day of the Hebrew month of Iyar.
According to some Rishonim ...
, bonfires are lit on to commemorate the Mishnaic
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah ...
sage Rabbi Shimon Bar Yochai
Shimon bar Yochai ( Zoharic Aramaic: שמעון בר יוחאי, ''Shim'on bar Yoḥai'') or Shimon ben Yochai (Mishnaic Hebrew: שמעון בן יוחאי, ''Shim'on ben Yoḥai''), also known by the acronym Rashbi, was a 2nd-century ''tannaiti ...
who according to tradition died on Lag BaOmer
Lag BaOmer ( he, , ''LaG Bāʿōmer''), also Lag B'Omer or Lag LaOmer, is a Jewish religious holiday celebrated on the 33rd day of the Counting of the Omer, which occurs on the 18th day of the Hebrew month of Iyar.
According to some Rishonim ...
. Rabbi Shimon Bar Yochai is accredited with having composed the Kabalistic
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The defi ...
work The Zohar (literally "The Shining" - hence the custom of lighting fire to commemorate him). The main celebration takes place at Rabbi Shimon's tomb on Mount Meron
Mount Meron ( he, הַר מֵירוֹן, ''Har Meron''; ar, جبل الجرمق, ''Jabal al-Jarmaq'') is a mountain in the Upper Galilee region of Israel. It has special significance in Jewish religious tradition and parts of it have been decla ...
in northern Israel, but all over the country bonfires are lit in open spaces. Linked by Modern Jewish tradition to the Bar Kokhba Revolt against the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
(132-135 CE), Lag BaOmer
Lag BaOmer ( he, , ''LaG Bāʿōmer''), also Lag B'Omer or Lag LaOmer, is a Jewish religious holiday celebrated on the 33rd day of the Counting of the Omer, which occurs on the 18th day of the Hebrew month of Iyar.
According to some Rishonim ...
is very popularly observed and celebrated as a symbol for the fighting Jewish spirit. As Lag Ba'Omer draws near, children begin collecting material for the bonfire: wood boards and planks, old doors, and anything else made of wood. On the night itself, families and friends gather round the fires and youths will burn their bonfires till daybreak.
Italy
InNortheast Italy
Northeast Italy ( it, Italia nord-orientale or just ) is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first level NUTS region and a European Parliament constituency. Northeast ...
, the celebration (in English "bread and wine"), and is held on the evening of Epiphany
Epiphany may refer to:
* Epiphany (feeling), an experience of sudden and striking insight
Religion
* Epiphany (holiday), a Christian holiday celebrating the revelation of God the Son as a human being in Jesus Christ
** Epiphany season, or Epiph ...
(5 January). A straw witch dressed with old clothes is placed on a bonfire and burned to ash. The witch symbolizes the past and the direction of the smoke indicates whether the new year is going to be good or bad.
The Northern Italian ("the old lady") is a version of the wicker man
A wicker man was purportedly a large wicker statue in which the druids (priests of Celtic paganism) sacrificed humans and animals by burning. The main evidence for this practice is a sentence by Roman general Julius Caesar in his '' Commentary ...
bonfire effigy, which is burned once a year as part of town festivals. As depicted in the film by Federico Fellini, it has a more pagan-Christian connotation when it is burned on Mid-Lent
Lent ( la, Quadragesima, 'Fortieth') is a solemn religious observance in the liturgical calendar commemorating the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke ...
Thursday.
In Abbadia San Salvatore
Abbadia San Salvatore is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Siena in the Italian region Tuscany, located about southeast of Florence and about southeast of Siena, in the area of Monte Amiata.
The town is named after the Abbey of th ...
, a village in the south of Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
, bonfires called up to seven meters high are burned during Christmas Eve to warm up people around them waiting for the midnight, following a millenary tradition.
In Southern Italy, traditionally bonfires are lit in the night between 16 and 17 January, thought to be the darkest and longest night of the year. The celebration is also linked to the cult of Saint Anthony The Great
Anthony the Great ( grc-gre, Ἀντώνιος ''Antṓnios''; ar, القديس أنطونيوس الكبير; la, Antonius; ; c. 12 January 251 – 17 January 356), was a Christian monk from Egypt, revered since his death as a saint. He is d ...
.
Japan
Every 16 August, the ancient city ofKyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin, Keihanshin metropolitan area along wi ...
holds the Gozan no Okuribi
, more commonly known as , is a festival in Kyoto, Japan. It is the culmination of the Obon festival on August 16, in which five giant bonfires are lit on mountains surrounding the city. It signifies the moment when the spirits of deceased famil ...
, a Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
bonfire-based spectacle, which marks the end of the *O-Bon
or just is fusion of the ancient Japanese belief in ancestral spirits and a Japanese Buddhist custom to honor the spirits of one's ancestors. This Buddhist–Confucian custom has evolved into a family reunion holiday during which people retu ...
season.
Luxembourg
The Luxembourgish town ofRemich
Remich ( lb, Réimech ) is a commune with town status in south-eastern Luxembourg with a population of 3,645 inhabitants . It is the capital of the canton of Remich. Remich lies on the left bank of the river Moselle, which forms part of the borde ...
annually holds a three-day-long celebration for Carnival (called in Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish ( ; also ''Luxemburgish'', ''Luxembourgian'', ''Letzebu(e)rgesch''; Luxembourgish: ) is a West Germanic language that is spoken mainly in Luxembourg. About 400,000 people speak Luxembourgish worldwide.
As a standard form of th ...
). The celebration of the Remich Fuesend Karneval celebrations concludes with the Buergbrennen, a bonfire that marks the end of winter. Such bonfires are also organised by others towns and villages throughout Luxembourg around the same time, although they only last an evening.
Nepal
 Bonfire in Nepal is taken almost synonymous with camp-fire. During winter months its quite common to have a bonfire in hotels, resorts, and residential areas, as well as private properties.
Bonfires are also lit during Siva ratri in the evening. This holiday is based on the lunar calendar and often falls during month of February.
Bonfire in Nepal is taken almost synonymous with camp-fire. During winter months its quite common to have a bonfire in hotels, resorts, and residential areas, as well as private properties.
Bonfires are also lit during Siva ratri in the evening. This holiday is based on the lunar calendar and often falls during month of February.
Nordic Countries
InIceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, bonfires are traditional on New Year's Eve, and on 6 January, which is the last day of the Icelandic Christmas season. In Norway and Denmark, large bonfires are lit on 23 June to celebrate or the evening before John the Baptist's birthday. As with many other traditions in Scandinavia, St. Hans is believed to have a pagan origin, the celebration of midsummer's eve.
In Sweden, Walpurgis Night
Walpurgis Night (), an abbreviation of Saint Walpurgis Night (from the German ), also known as Saint Walpurga's Eve (alternatively spelled Saint Walburga's Eve), is the eve of the Christian feast day of Saint Walpurga, an 8th-century abbess ...
is celebrated on 30 April, and festivities include the burning of a bonfire. In Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, Midsummer Eve is celebrated with large bonfires.
Lithuania
In Lithuania bonfires are lit to celebrate St John's Eve (aka: (Dew Holiday)) during themidsummer
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer usually held at a date around the summer solstice. It has pagan pre-Christian roots in Europe.
The undivided Christian Church designated June 24 as the feast day of the early Christian martyr ...
festival . Bonfires may be lit to keep witches and evil spirits away.
Poland
 In
In Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, bonfires are traditionally and still enthusiastic burned during ''Feast of Saints Peter and Paul'', ''Pentecost'' day and ''Saint John Night'' as , (Śląsk
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
, Małopolska
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
, Podkarpacie
Subcarpathian Voivodeship or Subcarpathia Province (in pl, Województwo podkarpackie ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship, or province, in the southeastern corner of Poland. Its administrative capital and largest city is Rzeszów. Along w ...
), ''Palinocka'' (Warmia
Warmia ( pl, Warmia; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian: ''Warńija''; lt, Varmė; Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia. Its historic capital ...
, Mazury
Masuria (, german: Masuren, Masurian: ''Mazurÿ'') is a ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the ...
, Kaszuby) or (Mazowsze
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
and Podlasie) on 23/24 June.
On 23 and 24 June, according to ancient custom, an immense number of Polish persons of both sexes repaired to the banks of the San (river)
The San ( pl, San; uk, Сян ''Sian''; german: Saan) is a river in southeastern Poland and western Ukraine, a tributary of the river Vistula, with a length of (it is the 6th-longest Polish river) and a basin area of 16,877 km2 (14,42 ...
, Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
and Odra river, to consult Fate respecting their future fortunes, jumping through a fire on the Eve of Saint John's was a sure way to health. The leaping of the youths over fire () must be a custom derived from remote antiquity. Jan Kochanowski
Jan Kochanowski (; 1530 – 22 August 1584) was a Polish Renaissance poet who established poetic patterns that would become integral to the Polish literary language. He is commonly regarded as the greatest Polish poet before Adam Mickiewicz.
...
, who died in 1584, mentions it in a song from an ancient tradition. Varro and Ovid relate, that in the Palilia
upright=1.5, ''Festa di Pales, o L'estate'' (1783), a reimagining of the Festival of Pales by Joseph-Benoît Suvée
The Parilia is an ancient Roman festival of rural character performed annually on 21 April, aimed at cleansing both sheep and sh ...
, celebrated in honour of the goddess Pales
In ancient Roman religion, Pales was a deity of shepherds, flocks and livestock. Regarded as male by some sources and female by others, ''Pales'' can be either singular or plural in Latin, and refers at least once to a pair of deities.
Pales' fes ...
, on 20 April, the anniversary of the foundation of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, the young Romans leaped over burning bundles of hay. In modern Italy, this kind of saltation is continued by the name of , though Pope Sergius III
Pope Sergius III (c. 860 − 14 April 911) was the bishop of Rome and nominal ruler of the Papal States from 29 January 904 to his death. He was pope during a period of violence and disorder in central Italy, when warring aristocratic factions ...
prohibited it.
Romania
InRomania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, in Argeș County, a bonfire is lit on the night of 25 October every year, as a tradition said to be done since the Dacians. It consists in burning of a tall tree, which resembles the body of a god. It is usually done on a high peak, in order to be seen from far away.
Slavic Europe
InBosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
and Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
, bonfires are traditionally lit on the evening before 1 May, commemorating Labour Day . Bonfires are also being built on the eve of the Christian holiday Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel ...
on so called Holy Saturday
Holy Saturday ( la, Sabbatum Sanctum), also known as Great and Holy Saturday (also Holy and Great Saturday), the Great Sabbath, Hallelujah Saturday (in Portugal and Brazil), Saturday of the Glory, Sabado de Gloria, and Black Saturday or Easter ...
and are lit next day early in the morning. This bonfires are called , or . The root, is the Serbo-Croatian word for Easter. Their burning symbolizes the Resurrection of Jesus
The resurrection of Jesus ( grc-x-biblical, ἀνάστασις τοῦ Ἰησοῦ) is the Christian belief that God raised Jesus on the third day after his crucifixion, starting – or restoring – his exalted life as Christ and Lo ...
. In villages far from cities, this tradition is still active. Young men and children all gather on some plane remote from village and start building a bonfire by collecting logs of wood, or pruned branches from vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineya ...
s and orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of ...
s. Bonfires are also lit on the evening before Saint George's Day
Saint George's Day is the feast day of Saint George, celebrated by Christian churches, countries, and cities of which he is the patron saint, including Bulgaria, England, Georgia, Portugal, Romania, Cáceres, Alcoy, Aragon and Catalonia.
Sai ...
on so called (in Croatia, on 24 April according to Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years dif ...
) or (in Serbia, on 6 May according to Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
). Idea for all this bonfires are probably taken from old Slavic tradition where bonfires were lit to celebrate the arrival of Spring.
In Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, bonfires are traditionally burned on 17 November.
Czech Republic and Slovakia
In theCzech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
, bonfires are also held on the last night of April and are called 'Phillip-Jakob's Night' () or "Burning of the Witches" (). They are considered to be historically linked with Walpurgis Night
Walpurgis Night (), an abbreviation of Saint Walpurgis Night (from the German ), also known as Saint Walpurga's Eve (alternatively spelled Saint Walburga's Eve), is the eve of the Christian feast day of Saint Walpurga, an 8th-century abbess ...
and Beltane
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking the ...
.
Turkey
In Turkey bonfires are lit onKakava Kakava is a celebration event of Romani people in Turkey. Its place of origin is East Thrace in Turkey.
Events
The belief that a Savior ''Baba Fingo'' would come and rescue them is immortal in the Romani folklore of the Romanlar in Turkey. It is ...
believed to be the awakening day of nature at the beginning of spring. Kakava is celebrated by the Romani people in Turkey
The Romani people in Turkey ( tr, Türkiye'deki Romanlar) or Turks of Romani Background ( tr, Roman kökenli Türk) are Turkish citizen and the biggest subgroup of the Turkish Roma, they are Sunni muslims, mostly of Sufism branch,https://acikb ...
on the night of 5-6 May.
United Kingdom
 In the
In the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and some Commonwealth countries, bonfires are lit on Guy Fawkes Night a yearly celebration held on the evening of 5 November to mark the failure of the Gunpowder Plot
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against King James I by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby who sough ...
of 5 November 1605, in which a number of Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
conspirators, including Guy Fawkes
Guy Fawkes (; 13 April 1570 – 31 January 1606), also known as Guido Fawkes while fighting for the Spanish, was a member of a group of provincial English Catholics involved in the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605. He was born and educated ...
, attempted to destroy the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminste ...
in London.
In Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
, bonfires are lit on Halloween, 31 October. and each 11 July, bonfires are lit by many Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
communities to celebrate the victory of Williamite
A Williamite was a follower of King William III of England (r. 1689–1702) who deposed King James II and VII in the Glorious Revolution. William, the Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, replaced James with the support of English Whigs.
O ...
forces at the Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ga, Cath na Bóinne ) was a battle in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II of England and Ireland, VII of Scotland, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and J ...
, which took place on 12 July 1690. This is often called the "Eleventh night
In Northern Ireland, the Eleventh Night or 11th Night, also known as "bonfire night", is the night before the Twelfth of July, an Ulster Protestant celebration. On this night, large towering bonfires are lit in Protestant loyalist neighbourhood ...
". Bonfires have also been lit by Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
communities on 9 August since 1972 to protest and commemorate Internment.
Historically in England, some time before 1400, fires were lit around Midsummer
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer usually held at a date around the summer solstice. It has pagan pre-Christian roots in Europe.
The undivided Christian Church designated June 24 as the feast day of the early Christian martyr ...
as a wake in the vigil for St John the Baptist
John the Baptist or , , or , ;Wetterau, Bruce. ''World history''. New York: Henry Holt and Company. 1994. syc, ܝܘܿܚܲܢܵܢ ܡܲܥܡܕ݂ܵܢܵܐ, Yoḥanān Maʿmḏānā; he, יוחנן המטביל, Yohanān HaMatbil; la, Ioannes Bapti ...
. Folk would awake in the evening, and make three manners of fire: one with only clean bones ("bonys") and no wood called a "bonnefyre", one with clean wood and no bones called a "wakefyre", and the third with both bones and wood, called "Saynt Ionys Fyre". Apparently the original wake fell into "lechery and gluttony", so the church deemed it instead as a fast.
 The annual rock and dance music
The annual rock and dance music Wickerman Festival
The Wickerman Festival was an annual music festival held near Auchencairn in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. Dubbed "Scotland's Alternative Music festival", its motto was "The Wickerman Festival – it's better than it needs to be!"
It bega ...
takes place in Kirkcudbrightshire
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative count ...
, Scotland. Its main feature is the burning of a large wooden effigy on the last night. The Wickerman festival is inspired by the horror film ''The Wicker Man
''The Wicker Man'' is a 1973 British folk horror film directed by Robin Hardy and starring Edward Woodward, Britt Ekland, Diane Cilento, Ingrid Pitt, and Christopher Lee. The screenplay by Anthony Shaffer, inspired by David Pinner's 1967 ...
'', a film itself inspired by the Roman accounts of the Celtic Druids ritual burning of a wicker effigy.
A ship is also burnt as part of the mid-winter Up Helly Aa
Up Helly Aa ( ; literally "Up Holy .html" ;"title="ay/nowiki>">ay/nowiki> All") is a type of fire festival held annually from January to March in various communities in Shetland, Scotland, to mark the end of the Yule season. Each festival inv ...
festival.
In Biggar, Lanarkshire, a bonfire is lit on Hogmanay (New Year's Eve) to celebrate the end of the old year and the beginning of the New Year. The bonfire takes almost a month to build using whatever combustible materials can be found. It is lit by a senior citizen of the town who is accompanied to the bonfire site (which is by the Corn Exchange in the centre of the town) by the local pipe band and several torchbearers. The celebrations are attended by hundreds of drinking and dancing revellers. During the war years, when a bonfire wasn't allowed, a candle was lit in a biscuit tin to keep the tradition of "burnin' oot the auld year" alive.
United States
 In
In New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
, on the night before the Fourth of July
Independence Day (colloquially the Fourth of July) is a federal holiday in the United States commemorating the Declaration of Independence, which was ratified by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, establishing the United States ...
, towns competed to build towering pyramids, assembled from hogsheads
A hogshead (abbreviated "hhd", plural "hhds") is a large cask of liquid (or, less often, of a food commodity). More specifically, it refers to a specified volume, measured in either imperial or US customary measures, primarily applied to alcoho ...
, barrels and casks
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
. They were lit at nightfall, to usher in the celebration. The highest were in Salem, Massachusetts
Salem ( ) is a historic coastal city in Essex County, Massachusetts, located on the North Shore of Greater Boston. Continuous settlement by Europeans began in 1626 with English colonists. Salem would become one of the most significant seaports tr ...
, composed of as many as forty tiers of barrels. The practice flourished in the 19th and 20th centuries, and can still be found in some New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
towns.
On Christmas Eve in Southern Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, bonfires are built along the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
levees to light the way for Papa Noël as he moves along the river in his pirogue
A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small boats, particularly dugouts and native canoes. The word is French and is derived from Spanish , which comes from the Carib '. Description
The term 'pirogue' does n ...
(Cajun
The Cajuns (; French: ''les Cadjins'' or ''les Cadiens'' ), also known as Louisiana ''Acadians'' (French: ''les Acadiens''), are a Louisiana French ethnicity mainly found in the U.S. state of Louisiana.
While Cajuns are usually described as ...
canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the ter ...
) pulled by eight alligator
An alligator is a large reptile in the Crocodilia order in the genus ''Alligator'' of the family Alligatoridae. The two extant species are the American alligator (''A. mississippiensis'') and the Chinese alligator (''A. sinensis''). Additiona ...
s. This tradition is an annual event in St. James Parish, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
.
(See Aggie Bonfire
The Aggie Bonfire was a long-standing annual tradition at Texas A&M University as part of the college rivalry with the University of Texas at Austin. For 90 years, Texas A&M students—known as Texas A&M Aggies, Aggies—built a bonfire on campu ...
)
One of the oldest traditions at Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, or TAMU) is a public, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of the Texas A&M University System in 1948. As of late 2021, T ...
involves the building of a bonfire by students to be burnt before their annual game against The University of Texas
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
. The tradition began in 1909 as little more than a burning trash pile. Eventually students began clearing land in the area, by hand, to harvest thousands of logs needed for its construction. In 1969 Aggie Bonfire
The Aggie Bonfire was a long-standing annual tradition at Texas A&M University as part of the college rivalry with the University of Texas at Austin. For 90 years, Texas A&M students—known as Texas A&M Aggies, Aggies—built a bonfire on campu ...
set a Guinness world record for tallest bonfire at 109 feet. In 1999, there was an accident
An accident is an unintended, normally unwanted event that was not directly caused by humans. The term ''accident'' implies that nobody should be blamed, but the event may have been caused by unrecognized or unaddressed risks. Most researche ...
where the stack collapsed during construction, killing 12 people and injuring 27 others. The accident led to the university to no longer sanction the building of Bonfire. Since 2002, the student-sponsored group Student Bonfire began building an annual bonfire in the spirit of the original.
Farm and garden bonfires
Bonfires are used on farms, in large gardens and allotments to dispose of waste plant material that is not readily composted. This includes woody material, perniciousweed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place", or a plant growing where it is not wanted.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. ...
s, disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
d material and material treated with persistent pesticides and herbicides. Such bonfires may be quite small but are often designed to burn slowly for several days so that wet and green material may be reduced to ash by frequently turning the unburnt material into the centre. Such bonfires can also deal with turf and other earthy material. The ash from garden bonfires is a useful source of potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
and may be beneficial in improving the soil structure of some soils although such fires must be managed with safety in mind. Garden and farm bonfires are frequently smoky and can cause local nuisance if poorly managed or lit in unsuitable weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmos ...
conditions.
See also
*Aggie Bonfire
The Aggie Bonfire was a long-standing annual tradition at Texas A&M University as part of the college rivalry with the University of Texas at Austin. For 90 years, Texas A&M students—known as Texas A&M Aggies, Aggies—built a bonfire on campu ...
; includes 1999 disaster that killed 12 people when it collapsed during construction
* Bonfire Rally
* Easter Fire
* Bonfires of Saint John
* Burning Man
* Effigy
*Fire ritual
Worship or deification of fire (also pyrodulia, pyrolatry or pyrolatria) is known from various religions. Fire has been an important part of human culture since the Lower Paleolithic. Religious or animist notions connected to fire are assumed ...
*Fireworks
Fireworks are a class of low explosive pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a large number of devices ...
*Gozan no Okuribi
, more commonly known as , is a festival in Kyoto, Japan. It is the culmination of the Obon festival on August 16, in which five giant bonfires are lit on mountains surrounding the city. It signifies the moment when the spirits of deceased famil ...
*Holi
Holi (), also known as the Festival of Colours, the Festival of Spring, and the Festival of Love,The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...". is an ancient Hindu religious festival ...
*Marzanna
Marzanna (in Polish), Morė (in Lithuanian), Marena (in Russian), Mara (in Ukrainian), Morana (in Czech, Slovene and Serbo-Croatian), Morena (in Slovak and Macedonian) or Mora (in Bulgarian) is a pagan Slavic goddess associated with seasonal r ...
*Need-fire
Need-fire, or Wild-fire (german: Notfeuer, goh, nodfyr, gd, tein'-éigin, russian: Живой огонь) is a term used in folklore to denote a superstition which has survived in the Scottish Highlands until recently.
Like the fire-churning s ...
* Piano burning
*Sussex Bonfire Societies
The Sussex Bonfire Societies are responsible for the series of bonfire festivals concentrated on central and eastern Sussex, with further festivals in parts of Surrey and Kent from September to November each year.
The celebrations mark both Guy ...
*Wicker man
A wicker man was purportedly a large wicker statue in which the druids (priests of Celtic paganism) sacrificed humans and animals by burning. The main evidence for this practice is a sentence by Roman general Julius Caesar in his '' Commentary ...
* Burgbrennen (Luxembourg)
* Hüttenbrennen (Eifel)
* Osterfeuer (German custom at Easter)
* Sechseläuten
The ''Sechseläuten'' (Zürich German: ''Sächsilüüte'', "The six o'clock ringing of the bells") is a traditional spring holiday in the Swiss city of Zürich celebrated in its current form, usually on the 3rd Monday of April, since the early 2 ...
(Swiss custom in Zürich)
* Biikebrennen (North Frisia)
References
External links
Dancing May Day Through History
{{Authority control Halloween events Seasonal traditions Summer traditions Types of fire